Last time, we talked about how to reverse engineer a binary using Ghidra. But what if you wanted to make modifications to the binary itself?
The process of making changes to a binary and modifying its instruction flow is called “patching a binary”. Hackers do this to bypass built-in protections, or to make the program behave in a different way to make the exploit development process go more smoothly.
And today, let’s talk about how to do this directly in Ghidra!
Crash Course Assembly
To patch a binary in Ghidra, you first have to gain an understanding of assembly language.
When a computer is executing code, it only understands machine code instructions. An executable binary is in this form.
Assembly language refers to any low-level programming language where there is a strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture’s machine code instructions. Reading assembly code helps us understand exactly how a program works and how the program interfaces with the machine’s resources.
Ghidra is equipped with a disassembler that translates machine language into assembly language. This makes the program flow more readable and helps us with the analysis process.
In assembly, instructions are generally formatted like so:
<operation> <list of arguments>
Here are a few of the most commonly used instructions:
mov <source>, <destination> - Move data from source to destination
push <source> - Push source onto stack
pop <destination> - Pop top of stack into destination
add <source>, <destination> - Add source to destination
jmp <location> - Jump to location
je/jz <location> - Jump if equal/zero
jne/jnz <location> - Jump if not equal/nonzero
ret - Pop return address from stack and jump to there
Patching A Binary
When Ghidra analyzes a binary, it disassembles the machine language back to assembly language. You can see the assembly instructions in the listing view after you open the file in Ghidra:
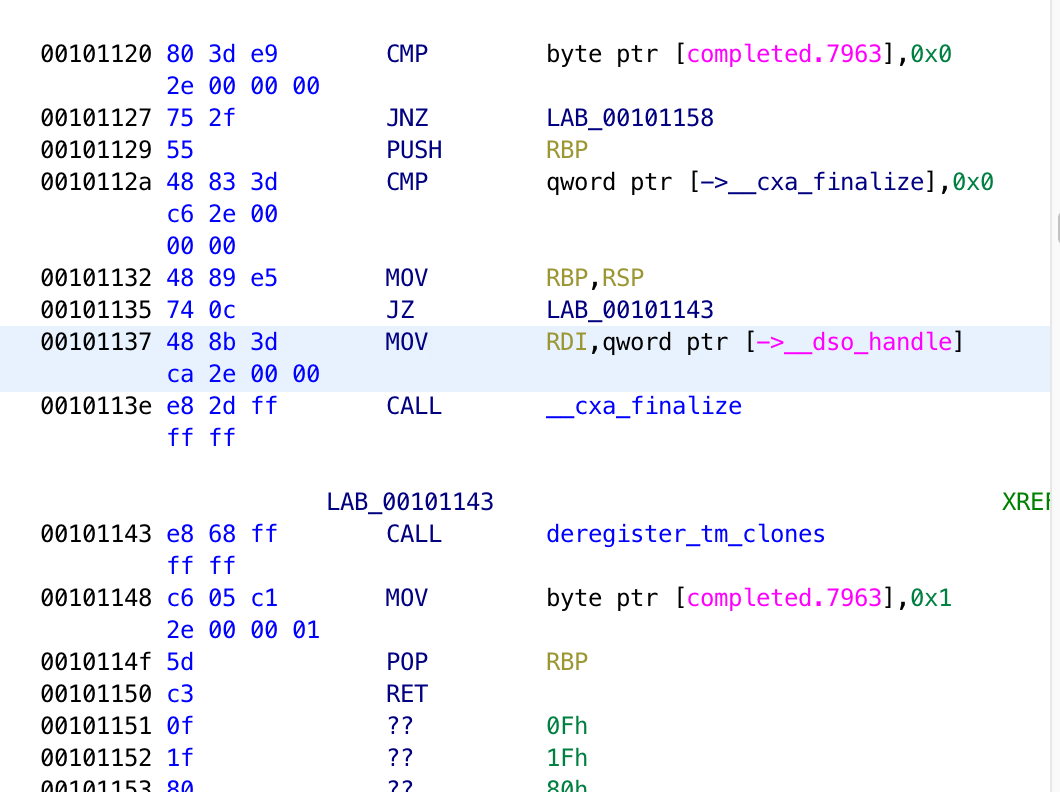
To patch an instruction, right-click on the instruction you want to modify and go to “Patch Instruction”. From there, you will see textboxes that you can type into.
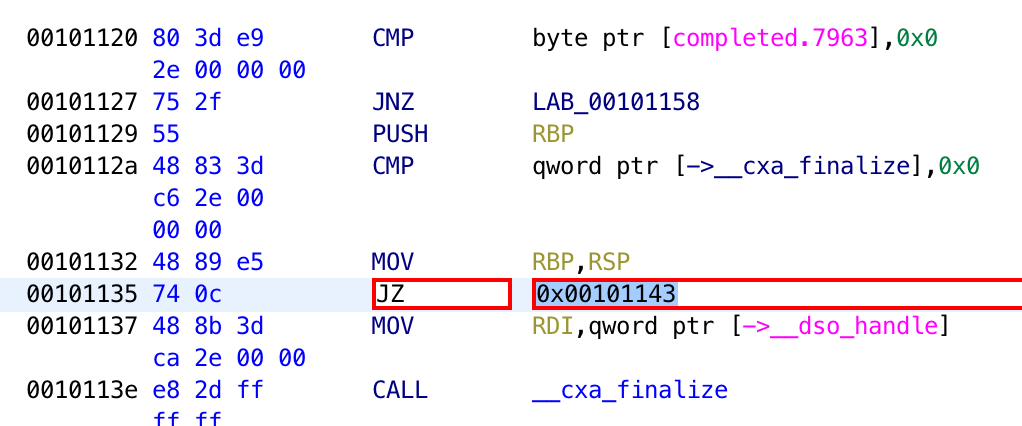
Finally, you can modify the instruction directly in the listing view.
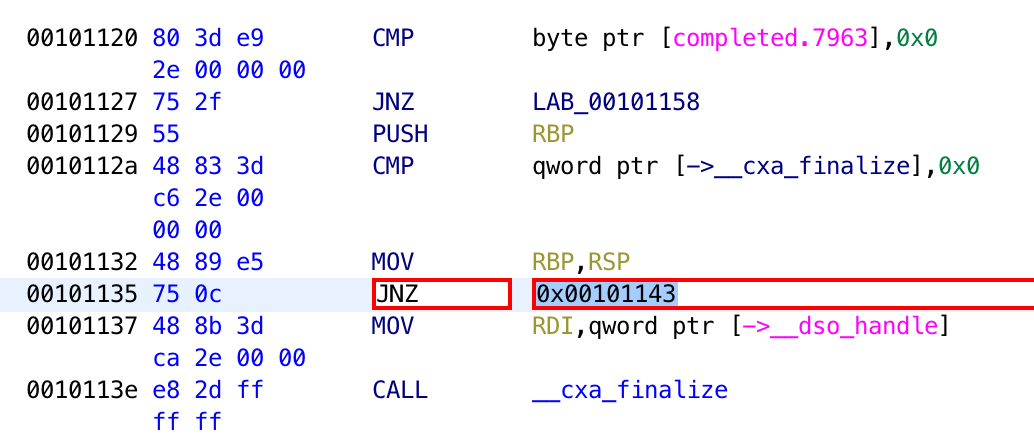
Saving The Patch
To save a binary that you have patched in Ghidra, you can use SavePatch:
schlafwandler/ghidra_SavePatch
This is a workaround script that addresses some issues that Ghidra has had in saving patched binaries. It saves the modifications that you made in Ghidra back to the binary.
To install this script, you can copy the “SavePatch.py” file in the repository into your Ghidra scripts directory. You can find the Ghidra scripts directory by going to the script manager on top of your Ghidra window.
Then, go to “Create New Script”.
Select “Python” and click “OK”. You should see the path of the Ghidra Scripts directory there. Move the SavePatch.py file to this directory.
To use the script to save your patched instructions, select the patched lines in the listing window. Since the script does not support saving multiple patches at the same time, you have to make all your modifications into one patch. So when patching multiple instructions, you need to select everything from one patched instruction to another patched instruction. Finally, go to Script Manager again to run the SavePatch.py script.
Conclusion
Ghidra is not simply a binary analysis tool, you can also use it to patch said binaries!
There are many more features in Ghidra that you can discover: including a powerful extension module, and a variety of features designed to streamline the binary analysis process. In this post, we went through how to use Ghidra to patch a binary. Good luck with your journey using Ghidra!